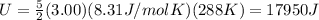The internal energy of an ideal gas is given by:
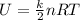
where
n is the number of moles
R is the gas constant
T is the absolute temperature of the gas
k=3 for monoatomic gases, k=5 for diatomic gases
In this problem, we have n=3.0 mol of a diatomic gas (k=5) at T=288 K. Substituting these numbers into the equation, we find the internal energy of the gas: