Answer:
Explanation:
Given that a value of a measurement is distributed with mean 200 and standard deviation 5.
Let X be the value of measurement
X is N(200,5)
a) The probability that a single measurement exceeds 201.
=
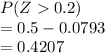
b)The probability that an average of 100 measurements exceeds 201
=
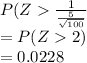
c) Can part (a) be answered if we drop the assumption that the distribution is normal?
No, we cannot. For a single item only if normal distribution is given we can do this.
d) Can part (b) be answered if we drop the assumption that the distribution is normal?
Yes, because when sample sizes are large, the mean follows normal irrespective of original distribution