Answer:
a) the intervals where f is increasing is
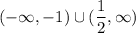
the intervals where f is decreasing is
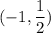
b)
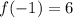 : local maximum
: local maximum
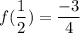 : local minimum
: local minimum
c) The inflection point :
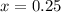
the range of concavity is:
Explanation:
This is a positive cubic function, (positive only means that the sign of the highest power term is +ve, nothing too fancy, its just to visualize the shape of the curve)
the positive sign tells you that this curve is coming from negative y to positive y when looking from left to right.
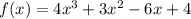
we can find the intervals where it is increasing and decreasing by knowing where this function has its stationary points (or turning points), in other words where
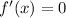
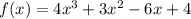
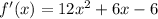
this is the function's first derivative. To find the stationary values, set
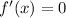
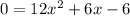
now solve for x
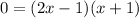
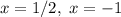
we can find the local minimum and maximum values of f by plugging in these value in the original function f(x):
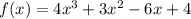
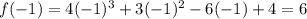 local maximum
local maximum
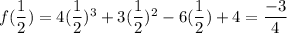 local minimum
local minimum
We also have enough information to show the intervals at which f(x) is increasing or decreasing
Since this is a positive cubic curve, the plot is coming up from negative infinity of the y-axis all the way upto x= -1, then turns back down until it reaches x=1/2, then finally turns up again to positive infinity of the y-axis.
so,
the intervals where f is increasing is
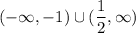
the intervals where f is decreasing is
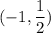
Concavity and Inflection Points
Now, we can go further in by differentiating our
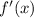
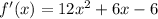
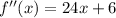
we can put the values we obtained of x from
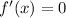 to find the curvature(or shape) of the curve at those points
to find the curvature(or shape) of the curve at those points
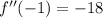
this is a negative value, it shows that at this value of x, the curve looks like this:
 (this is known a concave shape)
(this is known a concave shape)
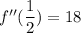
this this is a positive value, it shows that at this value of x, the curve looks like this:
 (this is knows as the convex shape)
(this is knows as the convex shape)
with this much information we have some idea about the concavity. (i.e, for what range of x does the curve maintain
 shape and for what range of x the curve maintains
shape and for what range of x the curve maintains
 shape?)
shape?)
we know that for the intervals
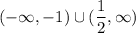 the curve is increasing, but the shape remains like
the curve is increasing, but the shape remains like
 even after this range.
even after this range.
So what we need is a point where the two shapes begin to change:
and that is the inflection point:
to put in terms of math: the inflection point is where:
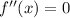
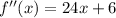
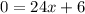
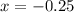
this is the point where concave turns to convex.
the inflection point is:
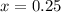
the range of concavity is:
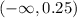
for fun we can also find the range of convexity
the range of convexity is:
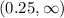
hopefully, this was helpful and a fun read.