Step-by-step explanation:
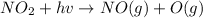
The maximum wavelength of light that can cause this reaction is 420 nm.
a) The wavelength given lies in the range of visible light range that is from 400 nano meters to 700 nano meters.
The light with wavelength of 420 nm is found in the range of visible light.
b)The maximum strength of a bond :
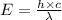
where,
E = energy of photon = Energy required to break single molecule of nitrogen dioxide
h = Planck's constant =
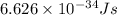
c = speed of light =
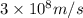
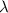 = wavelength =
= wavelength =
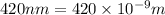
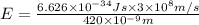
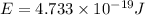
Energy required to break 1 mole of nitrogen dioxide molecules:
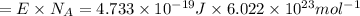
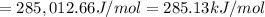
(1 J = 0.001 kJ )
285.13 is the maximum strength of a bond, in kJ/mol, that can be broken by absorption of a photon of 420-nm light.
c) the photodissociation reaction showing Lewis-dot structures is given in an image attached.