Answer:
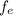 = 1.9 cm
= 1.9 cm
Step-by-step explanation:
The magnification of a microscope is the product of the magnification of the eyepiece by the magnifier with the objective
M = M₀
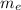
Where M₀ is the magnification of the objective and
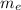 is the magnification of the eyepiece.
is the magnification of the eyepiece.
The eyepiece is focused to the near vision point (d = 25 cm)
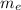 = 25 /
= 25 /
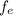
The objective is focused on the distances of the tube (L)
M₀ = -L / f₀
Substituting
M = - L/f₀ 25/
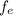
1) Let's look for the focal length of the eyepiece (faith)
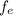 = - L 25 / f₀ M
= - L 25 / f₀ M
M = 400X = -400
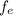 = - 12 25 /0.40 (-400)
= - 12 25 /0.40 (-400)
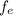 = 1.875 cm
= 1.875 cm
Let's approximate two significant figures
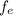 = 1.9 cm
= 1.9 cm