Answer:
The correct option is: C. 1.1 L
Step-by-step explanation:
Given: Temperature: T = 25°C = 25 +273 = 298K (∵ 1°C = 273K)
Pressure: P = 1 atm, Given mass of- CH₄: m₁ = 1g; O₂: m₂ = 3g
Volume: V= ?
Molar mass of CH₄: M₁ = 16g; O₂: M₂ = 32g
As Number of moles:
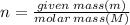
∴ Number of moles of CH₄:
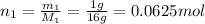
Number of moles of O₂:
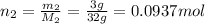
In the given reaction: CH₄(g) + 2O₂(g) → CO₂(g) + 2H₂O(l)
1 mole of methane (CH₄) reacts with 2 moles oxygen (O₂) to give 1 mole of CO₂.
So 0.0625 mol of CH₄ reacts with
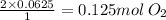 .
.
Thus the limiting reagent is O₂.
Now, 2 moles O₂ gives 1 mole of CO₂
So 0.0937 mol O₂ gives
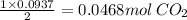
Therefore, the total number of moles of gas after the completion of the reaction: n = number of moles of CO₂: n₃ = 0.0468 mol
Now to calculate the volume of the balloon, we use the ideal gas law:
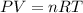
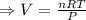
Here, R is the gas constant = 0.08206 L·atm/(mol·K)
T is Temperature,
P is Pressure,
n is Total number of moles of gas
and, V is Volume
Therefore, the volume of the balloon after the completion of the reaction:
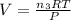
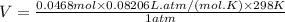
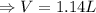
Therefore, the total volume of the balloon after the completion of the reaction: V = 1.14 L