Answer:
a)
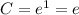
b)
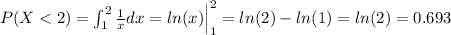
c)
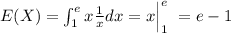
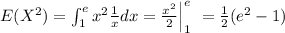
![Var(X)=E(X^2)-[E(X)]^2= (1)/(2)(e^2 -1) -(e-1)^2 = 0.242](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/jk720xzjoarq52tfuim53scf9tm3jp2o4w.png)
Explanation:
a) what must the value of C be so that f(x) is a probability density function?
In order to be a probability function we need this condition:
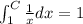
And solving the left part of the integral we have:
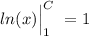
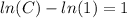 , so then
, so then
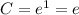
b) find P(X<2)
We can find this probability on this way using the density function:
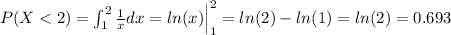
c) find E(X) and Var(X)
We can find the expected value on this way:
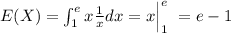
In order to find the Var(X) we need to find the second moment given by:
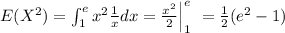
And now we can use the following definition:
![Var(X)=E(X^2)-[E(X)]^2= (1)/(2)(e^2 -1) -(e-1)^2 = 0.242](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/jk720xzjoarq52tfuim53scf9tm3jp2o4w.png)