Answer:
7908.92307 W
683330953.248 J
Step-by-step explanation:
k = Heat conduction coefficient = 0.8 W/(m·°C)
A = Area =
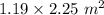
l = Thickness = 0.65 cm
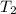 = 24°C
= 24°C
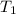 = 0°C
= 0°C
Rate of heat transfer is given by
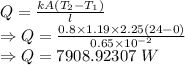
The rate of heat transfer is 7908.92307 W
Amount of energy is given by

The energy transferred through the window in one day is 683330953.248 J