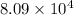Answer :
(a) The value of 'K' for the reaction is
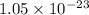
(b) The value of 'K' for the reaction is
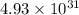
(c) The value of 'K' for the reaction is
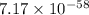
(d) The value of 'K' for the reaction is
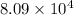
Explanation :
The relation between the equilibrium constant and standard Gibbs free energy is:
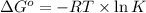
where,
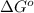 = standard Gibbs free energy
= standard Gibbs free energy
R = gas constant = 8.314 J/K.mol
T = temperature = 298 K
K = equilibrium constant
Now we have to calculate the value of 'K' for the following reactions.
(a)
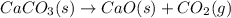
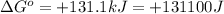
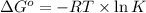
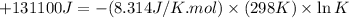
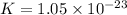
Thus, the value of 'K' for the reaction is
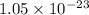
(b)
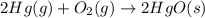
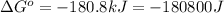
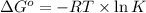
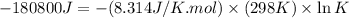
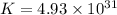
Thus, the value of 'K' for the reaction is
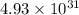
(c)
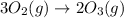
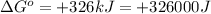
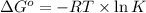
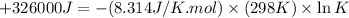
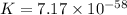
Thus, the value of 'K' for the reaction is
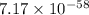
(d)
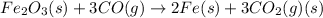
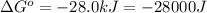
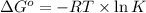
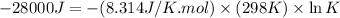
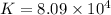
Thus, the value of 'K' for the reaction is