Answer:
Numbers of electrons transferred in the electrolytic or voltaic cell is 6 electrons.
Step-by-step explanation:
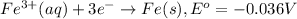
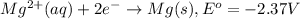
The substance having highest positive reduction
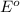 potential will always get reduced and will undergo reduction reaction.
potential will always get reduced and will undergo reduction reaction.
Reduction : cathode
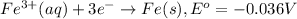 ..[1]
..[1]
Oxidation: anode
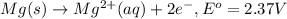 ..[2]
..[2]
Oxidation reaction occurs at anode and reduction reaction occurs at cathode.
To calculate the
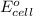 of the reaction, we use the equation:
of the reaction, we use the equation:
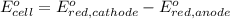
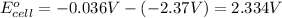
The overall reaction will be:
2 × [1] + 3 × [2] :

Electrons on both sides will get cancelled :
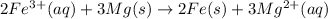
Numbers of electrons transferred in the electrolytic or voltaic cell is 6 electrons.