Answer:
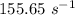 is the rate constant at a temperature of 30.0 °C.
is the rate constant at a temperature of 30.0 °C.
Step-by-step explanation:
Using the expression,
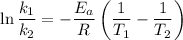
Wherem
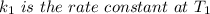
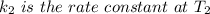
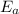 is the activation energy
is the activation energy
R is Gas constant having value = 8.314 J / K mol
Thus, given that,
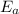 = 52 kJ/mol = 52000 J/mol (As 1 kJ = 1000 J)
= 52 kJ/mol = 52000 J/mol (As 1 kJ = 1000 J)
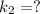
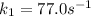
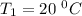
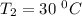
The conversion of T( °C) to T(K) is shown below:
T(K) = T( °C) + 273.15
So,
T = (20 + 273.15) K = 293.15 K
T = (30 + 273.15) K = 303.15 K
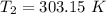
So,
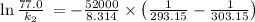
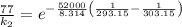
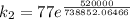
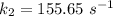
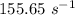 is the rate constant at a temperature of 30.0 °C.
is the rate constant at a temperature of 30.0 °C.