Answer:
The final speed become
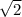 of the initial speed .
of the initial speed .
Step-by-step explanation:
We know that kinetic energy given as
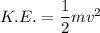
m=mass ,v=velocity
From work power energy theorem
Work done by all forces = Change in the kinetic energy
At initial condition
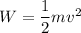 --------1
--------1
Lets take the final speed is v' when the work done become 2W
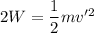 ---------2
---------2
From above two equation
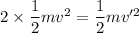
2 v² = v'²
Therefore we can say that
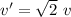
The final speed become
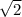 of the initial speed .
of the initial speed .