Answer :
Entropy of system = 94.6 J/K.mol
Entropy of surrounding = -94.6 J/K.mol
Entropy of universe = 0 J/K.mol
The process is a spontaneous process.
Explanation :
The given chemical reaction is:
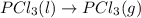
First we have to calculate the entropy of reaction
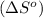 .
.
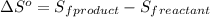
![\Delta S^o=[n_(PCl_3(g))* \Delta S^0_((PCl_3(g)))]-[n_(PCl_3(l))* \Delta S^0_((PCl_3(l)))]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/npbijg82j90aniqhb9asyj7uqxe0krxje2.png)
where,
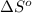 = entropy of reaction = ?
= entropy of reaction = ?
n = number of moles
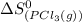 = standard entropy of formation of gaseous
= standard entropy of formation of gaseous
 = 311.7 J/K.mol
= 311.7 J/K.mol
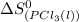 = standard entropy of formation of liquid
= standard entropy of formation of liquid
 = 217.1 J/K.mol
= 217.1 J/K.mol
Now put all the given values in this expression, we get:
![\Delta S^o=[1mole* (311.7J/K.mol)]-[1mole* (217.1J/K.mol)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/br8jmq703nnxr5oqwelseqpo6s1248v5q5.png)
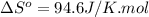
Entropy of reaction =
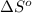 = Entropy of system = 94.6 J/K.mol
= Entropy of system = 94.6 J/K.mol
Entropy of system = -Entropy of surrounding = - 94.6 J/K.mol
As, we know that:
Entropy of universe = Entropy of system + Entropy of surrounding
Entropy of universe = 94.6 J/K.mol + (-94.6 J/K.mol)
Entropy of universe = 0
Now we have to calculate the enthalpy of reaction
 .
.
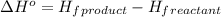
![\Delta H^o=[n_(PCl_3(g))* \Delta H^0_((PCl_3(g)))]-[n_(PCl_3(l))* \Delta H^0_((PCl_3(l)))]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/cy8qwuyt5c8onapl4vr4f82t3kcnq4ih1r.png)
where,
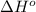 = enthalpy of reaction = ?
= enthalpy of reaction = ?
n = number of moles
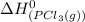 = standard enthalpy of formation of gaseous
= standard enthalpy of formation of gaseous
 = -319.7 kJ/mol
= -319.7 kJ/mol
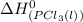 = standard enthalpy of formation of liquid
= standard enthalpy of formation of liquid
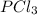 = -288.07 kJ/mol
= -288.07 kJ/mol
Now put all the given values in this expression, we get:
![\Delta H^o=[1mole* (-319.7kJ/mol)]-[1mole* (-288.07kJ/mol)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/l70kss9fbeocmx59kgyahhq8jof5enxywd.png)
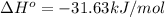
Now we have to calculate the Gibbs free energy.
As we know that,
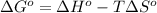
where,
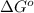 = standard Gibbs free energy = ?
= standard Gibbs free energy = ?
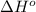 = standard enthalpy = -31.63 kJ = -31630 J
= standard enthalpy = -31.63 kJ = -31630 J
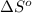 = standard entropy = -94.6 J/K
= standard entropy = -94.6 J/K
T = temperature of reaction =
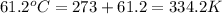
Now put all the given values in the above formula, we get:
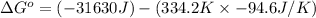

A reaction to be spontaneous when
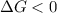
A reaction to be non-spontaneous when
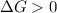
For the reaction to be spontaneous, the Gibbs free energy of the reaction
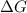 is negative or we can say that the value of
is negative or we can say that the value of
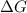 is less than zero.
is less than zero.
As the value of
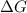 is less than zero that means the reaction is spontaneous.
is less than zero that means the reaction is spontaneous.