Answer:
A. twice as fast.
Step-by-step explanation:
m = Mass of skater
h = Height from where the skater starts
g = Acceleration due to gravity = 9.81 m/s²
Here the kinetic and potential energies balance each other
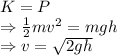
Velocity from 7 m
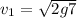
Velocity from 4 m
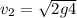
Dividing the two equations
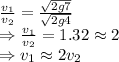
So, the velocity of the skater is twice as fast