Answer:
L=1.44T
Explanation:
We can determine c by knowing the lenght L and the temperature T which is given. We can determine c:
![L=180=m\cdot{150}+c[/tex}</p><p>[tex]180-m\cdot{150}=c](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/middle-school/v5t2v8yklvzn3z1pew7tcl3xfeqk38gc4a.png)
We can take any point to determine m, we can determine this by the ratio of length to temperature:
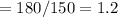
We know now that the lenght is 1.2 times the temperature. IF the the temperature is 50, the length is:
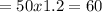
m is the gradient defined as (L2-L1)/(T2-T1) and we have all the terms:
[tex]m=(180-50)/(150-60)=130/90=1.44{tex]
We solve c by L=0:
c = 0