Step-by-step explanation:
The given data is as follows.
mass = 0.158 g, volume = 100 ml
Molarity = 1.0 M,
 =
=
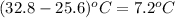
The given reaction is as follows.

So, moles of magnesium will be calculated as follows.
No. of moles =
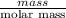
=
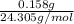
=

= 0.0065 mol
Now, formula for heat released is as follows.
Q =
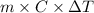
=
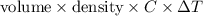
=
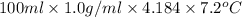
= 3010.32 J
Hence, heat of reaction will be calculated as follows.
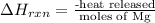
=

= -4.63 J/mol
or, =
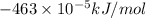 (as 1 kJ = 1000 J)
(as 1 kJ = 1000 J)
Thus, we can conclude that heat of given reaction is
 kJ/mol.
kJ/mol.