Answer:
The correct answer is option e.
Step-by-step explanation:
Total volume of the mixture of solution= 50.0 mL + 50.0 mL = 100.0 mL
Total mass of the solution = M
Density of the mixture of solution = density of pure water = d = 1 g/mL


Specific heat of mixture of solution = Specific of water = c
c = 4.184 J/g°C
Change in temperature = ΔT = 31.77°C - 25.10°C =6.67°C
Heat gained by the mixture of solution = Q
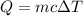

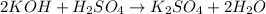
Moles of KOH = n
Volume of KOH solution = 50.0 mL = 0.050 L
Molarity of the solution = 1.00 M

The ΔH of this reaction:

The ΔH of this reaction is -55.8 kJ/mol.