Answer:
(a) x = 9, (9,4)
(b) x = 1, (1,3)
(c) x = 1 and the graph of f(x) and g(x) intersects at point (1,3)
(d)
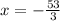 or x = 9
or x = 9
(e)
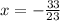
Explanation:
We are given that
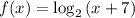 ....... (1),and
....... (1),and
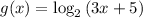 ........ (2)
........ (2)
Now,
(a) We have to solve f(x) = 4
⇒
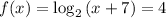
Converting logarithm to exponent form, we get,
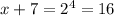
⇒ x = 9 (Answer)
Now, the point on the graph of f(x) will be (9,4) (Answer)
(b) We have to solve g(x) = 3
⇒
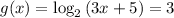
Converting logarithm to exponent form, we get,
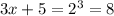
⇒ x = 1 (Answer)
Now, the point on the graph of g(x) will be (1,3) (Answer)
(c) We have to solve f(x) = g(x)
⇒
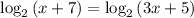
Now comparing both sides we can write
x + 7 = 3x + 5
⇒ 2x = 2
⇒ x = 1 (Answer)
Now, at x = 1,
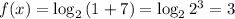
So, the graph of f(x) and g(x) intersects at point (1,3) (Answer)
(d) We have to solve (f + g)(x) = 9
⇒
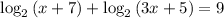
⇒
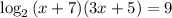
⇒
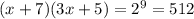
⇒ 3x² + 26x - 477 = 0
⇒ (3x + 53)(3x - 27) = 0
Hence,
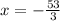 or x = 9 (Answer)
or x = 9 (Answer)
(e) We have to solve (f - g)(x) = 3
⇒
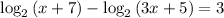
⇒
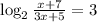
⇒
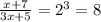
⇒ x + 7 = 24x + 40
⇒ 23x = - 33
⇒
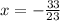 (Answer)
(Answer)