Answer:
The specific heat of magnesium is 1.04 J/g°C.
Step-by-step explanation:
Heat lost by the magnesium = Q
Mass of the magnesium = m = 62.08 g
Heat capacity of magnesium= c = ?
Initial temperature of the magnesium =
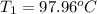
Final temperature of the magnesium= T = 35.60 °C
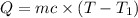
Heat absorbed by coffee cup calorimeter = Q'
Heat capacity of coffee cup calorimeter = C = 1.79 J/°C
Initial temperature of coffee cup calorimete =
 = 23.19°C
= 23.19°C
Final temperature of coffee cup calorimete = T = 35.60 °C
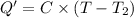
Heat absorbed by the water = q
Mass of water = m' = 77.81 g
Heat capacity of water = c' = 4.18 J/g°C
Initial temperature of water =
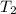 = 0°C
= 0°C
Final temperature of water = T
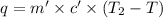
According law of conservation of energy , energy lost by coffee will equal to heat required to raise temperature of water and coffee cup calorimeter.
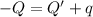
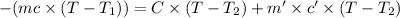
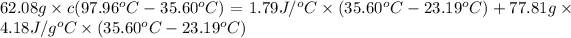
On solving we get:
c = 1.04 J/g°C
The specific heat of magnesium is 1.04 J/g°C.