Answer:

Step-by-step explanation:
Total heat released during reaction is equal to total heat gained by water and bomb calorimeter.
Let the heat released during reaction be q.
q = -16.0 kJ
Thus heat absorbed by calorimeter = + 16.0 kJ
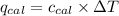
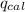 = Heat gained by calorimeter = 16000 J
= Heat gained by calorimeter = 16000 J
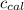 = Heat capacity of calorimeter = ?
= Heat capacity of calorimeter = ?
Change in temperature = ΔT = 2.22°C
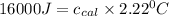
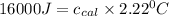
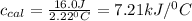
Thus heat capacity of a calorimeter is
