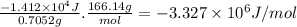Answer:
-3.327 × 10⁶ J/mol
Step-by-step explanation:
According to the law of conservation of energy, the sum of the energy released by the combustion and the energy absorbed by the calorimeter and the water is zero.
qcomb + qcal + qw = 0
qcomb = - (qcal + qw) [1]
The heat absorbed by the calorimeter (qcal) can be calculated using the following expression:
qcal = Ccal . ΔT = 823.0 J/°C . (24.01°C - 21.77°C) = 1.844 × 10³ J
where,
Ccal is the heat capacity of the calorimeter
ΔT is the difference in temperature
The heat absorbed by the water (qw) can be calculated using the following expression:
qw = cw . mw . ΔT = 4.184 J.g⁻¹.°C⁻¹ . 1.310 × 10³ g . (24.01°C - 21.77°C) = 1.228 × 10⁴ J
where,
cw is the heat capacity of water
mw is the mass of water
ΔT is the difference in temperature
From [1],
qcomb = - (qcal + qw) = -(1.844 × 10³ J + 1.228 × 10⁴ J) = -1.412 × 10⁴ J
The molar heat of combustion of phtalic acid is: