Answer: a) The maximum amount of dichloromethane
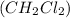 that can be formed is 29 grams.
that can be formed is 29 grams.
b) The formula for the limiting reagent is
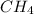
c) Amount of the excess reagent i.e
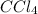 remains after the reaction is complete is 0.02 moles.
remains after the reaction is complete is 0.02 moles.
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the moles, we use the equation:
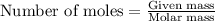
a) moles of
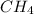
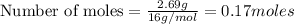
b) moles of
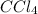
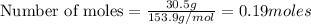
The balanced chemical equation will be:
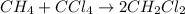
According to stoichiometry :
1 mole of
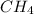 require 1 mole of
require 1 mole of
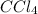
Thus 0.17 mole of
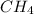 require=
require=
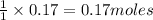 of
of
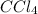
Thus
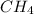 is the limiting reagent as it limits the formation of product and
is the limiting reagent as it limits the formation of product and
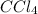 is the excess reagent as (0.19-0.17) =0.02 moles of
is the excess reagent as (0.19-0.17) =0.02 moles of
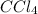 are left unreacted.
are left unreacted.
As 1 moles of
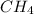 give = 2 moles of
give = 2 moles of
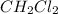
Thus 0.17 moles of
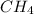 give =
give =
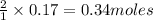 of
of
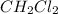
Mass of
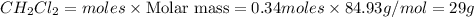
Thus 29 g of
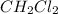 will be produced from the given masses of both reactants.
will be produced from the given masses of both reactants.