Answer: No, the reverse reaction must proceed to establish equilibrium.
Step-by-step explanation:
 is the constant of a certain reaction at equilibrium while
is the constant of a certain reaction at equilibrium while
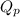 is the quotient of activities of products and reactants at any stage other than equilibrium of a reaction.
is the quotient of activities of products and reactants at any stage other than equilibrium of a reaction.
For the given chemical reaction:
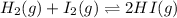
The expression of
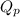 for above equation follows:
for above equation follows:
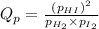
We are given:
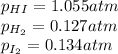
Putting values in above equation, we get:
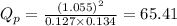
We are given:
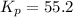
There are 3 conditions:
- When
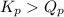 ; the reaction is product favored.
; the reaction is product favored. - When
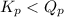 ; the reaction is reactant favored.
; the reaction is reactant favored. - When
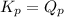 ; the reaction is in equilibrium.
; the reaction is in equilibrium.
As,
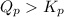 , the reaction will be favoring reactant side or the reaction must proceed in the reverse direction.
, the reaction will be favoring reactant side or the reaction must proceed in the reverse direction.
Hence, no, the reverse reaction must proceed to establish equilibrium.