Answer:
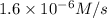 is the rate of formation of nitrogen dioxide.
is the rate of formation of nitrogen dioxide.
Step-by-step explanation:
Rate law says that rate of a reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of the reactants each raised to a stoichiometric coefficient determined experimentally called as order.
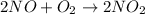
Given: Order with respect to
 = 1
= 1
Order with respect to
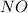 = 2
= 2
Thus rate law is:
![R=k[NO]^2[O_2]^1](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/basatfxlgmwq9mbxbx226n9s1lx6cg6dgc.png)
k= rate constant
![R=k[NO]^2[O_2]^1](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/basatfxlgmwq9mbxbx226n9s1lx6cg6dgc.png)
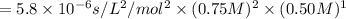
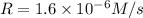
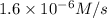 is the rate of formation of nitrogen dioxide.
is the rate of formation of nitrogen dioxide.