Answer: The concentration of iron (II) sulfate solution is 5.66 M
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the number of moles for given molarity, we use the equation:
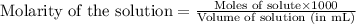 .....(1)
.....(1)
Molarity of potassium permanganate = 0.65 M
Volume of solution = 25.6 mL
Putting values in equation 1, we get:

Net ionic equation is defined as the equation in which no spectator ions are present in the reaction.
The net ionic equation for the reaction of potassium permanganate and iron (II) sulfate solution follows:
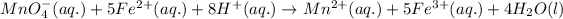
By Stoichiometry of the reaction:
1 mole of permanganate ions react with 5 moles of iron (II) ions
So, 0.017 moles of permanganate ions will react with =
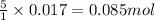 of iron (II) ions
of iron (II) ions
Now, calculating the concentration of iron (II) ions by using equation 1, we get:
Moles of iron (II) sulfate = 0.085 mol
Volume of solution = 15.0 mL
Putting values in above equation, we get:
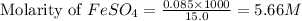
Hence, the concentration of iron (II) sulfate solution is 5.66 M