Answer:
The magnitude of the magnetic force exerted on the moving charge by the current in the wire is 2.18 x
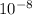 N
N
The direction of the magnetic force exerted on the moving charge by the current in the wire is radially inward
Step-by-step explanation:
given information:
current, I = 3 A
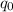 = +6.5 x
= +6.5 x
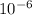 C
C
r = 0.05 m
v = 280 m/s
and direction of the magnetic force exerted on the moving charge by the current in the wire, we can use the following formula:
F = qvB sin θ
where
F = magnetic force (N)
q = electric charge (C)
v = velocity (m/s)
θ = the angle between the velocity and magnetic field
to find B we use
B = μ
 I/2πr
I/2πr
μ
 = 4π x
= 4π x
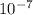 or 1.26 x
or 1.26 x
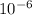 N/
N/
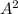 , thus
, thus
B = 4π x
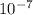 x 3 / 2π(0.05)
x 3 / 2π(0.05)
= 1.2 x
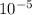 T
T
Now, we can calculate the magnitude force
F = qvB sin θ
θ = 90°, because the speed and magnetic are perpendicular
F = 6.5 x
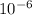 x 280 x 1.2 x
x 280 x 1.2 x
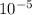 sin 90°
sin 90°
= 2.18 x
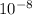 N
N
Using the hand law, the magnetic direction is radially inward