Answer:
the maximum concentration of the antibiotic during the first 12 hours is 1.185
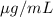 at t= 2 hours.
at t= 2 hours.
Explanation:
We are given the following information:
After an antibiotic tablet is taken, the concentration of the antibiotic in the bloodstream is modeled by the function where the time t is measured in hours and C is measured in
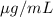
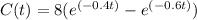
Thus, we are given the time interval [0,12] for t.
- We can apply the first derivative test, to know the absolute maximum value because we have a closed interval for t.
- The first derivative test focusing on a particular point. If the function switches or changes from increasing to decreasing at the point, then the function will achieve a highest value at that point.
First, we differentiate C(t) with respect to t, to get,
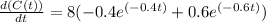
Equating the first derivative to zero, we get,
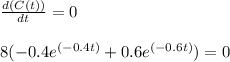
Solving, we get,
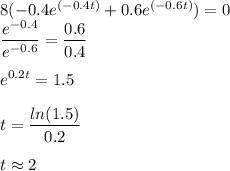
At t = 0
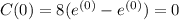
At t = 2
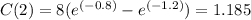
At t = 12
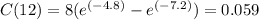
Thus, the maximum concentration of the antibiotic during the first 12 hours is 1.185
 at t= 2 hours.
at t= 2 hours.