Answer:
ksp = 0,176
Step-by-step explanation:
The borax (Na₂borate) in water is in equilibrium, thus:
Na₂borate(s) ⇄ borate²⁻(aq) + 2Na⁺(aq)
When you add just borax, the moles of Na²⁺ are twice the moles of borate²⁻, that means 2borate²⁻=Na⁺ (1)
The ksp is defined as:
ksp = [borate²⁻] [Na⁺]²
Then, borate²⁻(B₄O₇²⁻) reacts with HCl thus:
B₄O₇²⁻ + 2HCl + 5H₂O → 4H₃BO₃ + 2Cl⁻
The moles of HCl that reacts with B₄O₇²⁻ are:
0,500M×0,01200L = 6,00x10⁻³ mol of HCl
As two moles of HCl react with 1 mol of B₄O₇²⁻, the moles of B₄O₇²⁻ are:
6,00x10⁻³ mol of HCl×
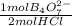 = 3,00x10⁻³ mol of B₄O₇²⁻
= 3,00x10⁻³ mol of B₄O₇²⁻
For (1), moles of Na⁺ are 3,00x10⁻³ mol ×2 = 6,00x10⁻³ mol of Na⁺
The [borate²⁻] is 3,00x10⁻³ mol of B₄O₇²⁻/0,00850L = 0,353M
And [Na⁺] is 6,00x10⁻³ mol of Na⁺ / 0,00850L = 0,706M
Replacing in the expression of ksp:
ksp = [0,353] [0,706]²
ksp = 0,176
I hope it helps!