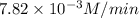Answer: The average rate of the reaction is
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the molarity of hydrogen gas generated, we use the equation:
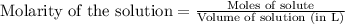
Moles of hydrogen gas =
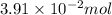
Volume of solution = 250 mL = 0.250 L (Conversion factor: 1 L = 1000 mL)
Putting values in above equation, we get:
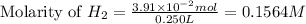
Average rate of the reaction is defined as the ratio of concentration of hydrogen generated to the time taken.
To calculate the average rate of the reaction, we use the equation:
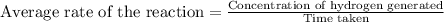
We are given:
Concentration of hydrogen generated = 0.1564 M
Time taken = 20.0 minutes
Putting values in above equation, we get:
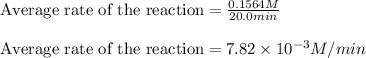
Hence, the average rate of the reaction is