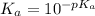Step-by-step explanation:
- Let lactic acid be represent as HA. And, pH is given as 2.75.
Hence, concentration of hydrogen ions will be calculated as follows.
pH =
![-log[H^(+)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/pclsb5d5ztpswphl1czegwokhxu5hzr3m7.png)
![[H^(+)] = 10^(-2.75)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/ba2pqdvcovz07dxx7haxozrd7r2c8ekry6.png)
=
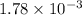 M
M
= 0.00178 M
The reaction equation will be as follows.
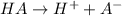
Initial: 0.025 0 0
Change: -0.00178 0.00178 0.00178
Equilibrium: 0.0232 0.00178 0.00178
Hence, calculate the value of
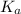 as follows.
as follows.
![K_(a) = ([H^(+)][A^(-)])/([HA])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/n80nhbilgynhw3qbdd82as81o4e09n26vi.png)
=
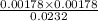
=
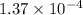
Therefore, value of the equilibrium constant is
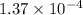 .
.
- Another method that we can use to determine the value of
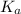 of any weak acid is when weak acid is titrating with a strong base then,
of any weak acid is when weak acid is titrating with a strong base then,
number of moles of acid = moles of salt formed by (acid + base)
These moles of salt are actually known as half equivalence point. So, at this point we need we need to measure the pH of solution with the help of a device called pH meter.
As we known that pH =
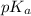
and,