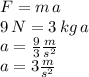Answer:
The acceleration is:
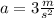
Step-by-step explanation:
To answer this, we need to recall Newton's Second Law of motion, that states that an object of mass m would accelerate (change its state of uniform motion) proportional to the force (F) that is applied , and exemplified by the following equation:
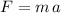
From here, and using the given values for mass (m = 3 kg) and force (F = 9 N), we can derive the value of the acceleration as shown below (notice that since all quantities are given in SI units, the resulting acceleration will also be in Si units (
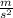 ):
):