Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
Magnetic field creates a force perpendicular to a moving charge in its field which is equal to Bev where B is magnetic field , e is amount of charge on the moving charge and v is the velocity of charge particle .
This force provides centripetal force for creation of circular motion. If r be the radius of the circular path
Bev = mv² / r
r = mv / Be
2 ) If an electron is accelerated by an electric field created by potential difference V then electric field
= V / d where d is distance between two points having potential difference v .
force on charged particle
electric field x charge
= V /d x e
work done by field
= force x distance
= V /d x e x d
V e
This is equal to kinetic energy created
V e = 1/2 mv²
= 1/2 m (r²B²e² / m² )
V = r²B²e/ 2 m
e / m = 2 V/ r²B²
3 )
B =
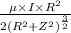
In Helmholtz coils , distance between coil is equal to R so Z = R/2
B =
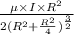
For N turns of coil and total field due to two coils
B =
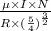
=
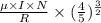
= 9.0 x 10^-7 NI/R