Answer : The value of
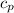 for reversible and adiabatic expansion is 55.04 J/mol.K
for reversible and adiabatic expansion is 55.04 J/mol.K
Explanation : Given,
Temperature at equilibrium =
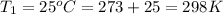
Pressure at equilibrium =
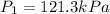
Temperature at adiabatic reversible expansion =
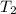
Pressure at adiabatic reversible expansion =
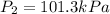
Temperature at constant volume process =
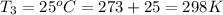
Pressure at constant volume process =
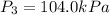
First we have to calculate the temperature at adiabatic reversible expansion.
Gay-Lussac's Law : It is defined as the pressure of the gas is directly proportional to the temperature of the gas at constant volume and number of moles.
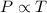
or,
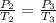
Now put all the given values in the above equation, we get:
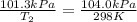
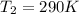
Now we have to calculate the value of
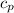 for reversible and adiabatic.
for reversible and adiabatic.
Formula used :
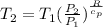
Now put all the given values in the above equation, we get:
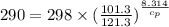
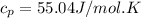
Therefore, the value of
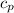 for reversible and adiabatic expansion is 55.04 J/mol.K
for reversible and adiabatic expansion is 55.04 J/mol.K