Answer:
The standard enthalpy of reaction = -4854.7kJ
The difference: ΔH-ΔE = Δ(PV) = Δn.R.T = 9910.288 J ≈ 9.91 kJ
Step-by-step explanation:
The balanced chemical equation for the combustion of heptane:
C₇H₁₆ (l) + 11 O₂ (g) → 7 CO₂ (g) + 8 H₂O (l)
Given: The standard enthalpy of formation (
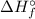 ) for: C₇H₁₆ (l) = -187.8 kJ/mol, O₂ (g) = 0 kJ/mol, CO₂ (g) = -393.5 kJ/mol, H₂O (l) = -286 kJ/mol
) for: C₇H₁₆ (l) = -187.8 kJ/mol, O₂ (g) = 0 kJ/mol, CO₂ (g) = -393.5 kJ/mol, H₂O (l) = -286 kJ/mol
To calculate the standard enthalpy of reaction (
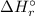 ) can be calculated by the Hess's law:
) can be calculated by the Hess's law:
![\Delta H _(r)^(\circ ) = \left [\sum \\u \cdot\Delta H _(f)^(\circ )(products) \right ] - \left [\sum \\u\cdot\Delta H _(f)^(\circ )(reactants) \right ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/vq71otuqn5qyoplqa6v0gz0wdf6azqi7f1.png)
Here,
 is the stoichiometric coefficient
is the stoichiometric coefficient
⇒
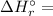
![\left [ 7* \Delta H _(f)^(\circ )\left (CO_(2)\right )+ 8* \Delta H _(f)^(\circ )\left (H_(2)O \right )\right ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/svavcufq4k5odkyoj3n8lie18wgb3xqzds.png)
![- \left [1* \Delta H _(f)^(\circ )\left (C_(7)H_(16)\right ) +11* \Delta H _(f)^(\circ )\left (O_(2) \right ) \right ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/eoflx778ws12lgwhcj2otnaqzje2gsft5p.png)
![=\left [ 7* \left (-393.5 kJ/mol \right )+ 8* \left (-286 kJ/mol \right )\right ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/86qsmhiklu2t2j59j750510ob2m1uiytck.png)
![-\left [1* \left (-187.8 kJ/mol \right ) +11* \left (0 kJ/mol \right ) \right ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/rntfo1twmu5ib7aqgq39jf38gbmdie9lsz.png)
⇒
![\Delta H _(r)^(\circ ) = \left [ \left (-2754.5 \right )+ \left (-2288 \right )\right ]\left -[ \left (-187.8 \right ) +\left (0 \right )\right ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/pgpyvb20jpalkor4aeob82kxzzf5btg84n.png)
⇒
![\Delta H _(r)^(\circ ) = \left [ -5042.5 ]\left -[ -187.8] = \left ( -4854.7kJ \right )](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/f7bk0dweh7h9rjlz2rvevsewg51h5sdfc0.png)
To calculate the difference: ΔH-ΔE=Δ(PV)
We use the ideal gas equation: P.V = n.R.T
⇒ ΔH-ΔE=Δ(PV) = Δn.R.T
Given: Temperature:T = 298K, R = 8.314 J⋅K⁻¹⋅mol⁻¹
Δn = number of moles of gaseous products - number of moles of gaseous reactants = (7)- (11) = (-4)
⇒ ΔH-ΔE=Δ(PV) = Δn.R.T = (-4 mol) × (8.314 J⋅K⁻¹⋅mol⁻¹) × (298K) = 9910.288 J = 9.91 kJ (∵ 1 kJ = 1000J )