To resolve point A and B we need the concepts related to conservation of momentum (By collision) and Kinetic Energy. Conservation of momentum is given by the equation,
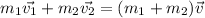
Our values in the statment are:
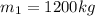
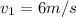
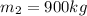
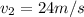
Part A) As it is in an icy intersection, there is two different components (x,y) then,
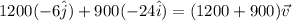
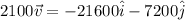
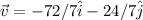
Then the magnitude is,
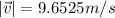
Part B) To obtain the Kinetic Energy Loss we need to use its equation, which is given by,
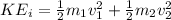
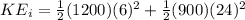
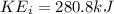
The final energy is given by,
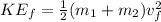
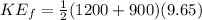
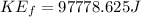
Then the change in Kinetic Energy is
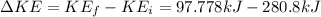
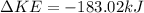
There was a loss of KE of 183.02kJ