Answer:
3000 Joule of work is to be done.
Option: b
Step-by-step explanation:
Given, mass of scooter = 20 Kg
Initial speed = 10 m/s, Final speed = 20 m/s, Work done = ΔE
Where, ΔE= change in kinetic energy
Solution:
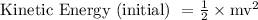
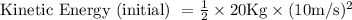
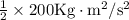 =
=
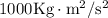
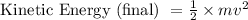
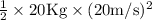
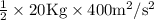
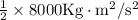
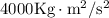
Work done = ΔE = Kinetic Energy (final) - Kinetic Energy (initial)
Work done = ΔE = 4000 J - 1000 J work done = ΔE = 3000J