Answer : The molar heat of solution for the salt is 452.9 kJ/mole
Explanation :
First we have to calculate the heat of solution.
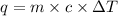
where,
q = heat of solution = ?
c = specific heat of water = specific heat of solution =
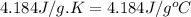
m = mass of solution = 107.093 g
- Mass of solution = Mass of water + Mass of salt
- Mass of solution = 100.000 g + 7.093 g = 107.093 g
 = change in temperature =
= change in temperature =
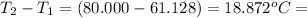
Now put all the given values in the above formula, we get:
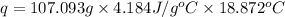
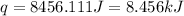
Now we have to calculate the molar heat of solution for the salt, in kJ/mol.
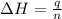
where,
 = molar heat of solution = ?
= molar heat of solution = ?
q = heat required = 8.456 kJ
m = mass of salt = 7.093 g
Molar mass of salt = 379.984 g/mol
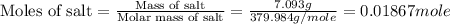
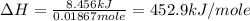
Therefore, the molar heat of solution for the salt is 452.9 kJ/mole