Answer:
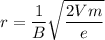
Step-by-step explanation:
Let m and e are the mass and charge of an electron. It is accelerated from rest through a potential difference V and are then deflected by a magnetic field that is perpendicular to their velocity. Let v is the velocity of the electron. It can be calculated as :
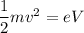
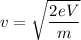
When the electron enters the magnetic field, the centripetal force is balanced by the magnetic force as :


or
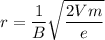
So, the radius of the resulting electron trajectory is
 . Hence, this is the required solution.
. Hence, this is the required solution.