The missing values in the table to investigate dilations of exponential functions include;
a = 1 b = 3
c = 1 d = 2
e = 6 f = 8
In Mathematics and Geometry, an exponential function can be modeled by using this mathematical equation:
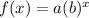
Where:
- a represents the initial value or y-intercept.
- x represents x-variable.
- b represents the rate of change or common ratio.
By substituting the given values of x (x-value) into the exponential function, we have the following;
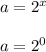
a = 1.
When x is 0, the value of b is given by;
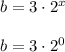
b = 3 × 1
b = 1.
When x is 0, the value of c is given by;
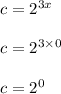
c = 1.
When x is 1, the value of d is given by;
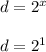
d = 2.
When x is 1, the value of e is given by;
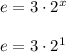
e = 3 × 2
e = 6.
When x is 0, the value of f is given by;
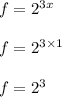
f = 8.
Complete Question;
Complete the table to investigate dilations of exponential functions.