Answer:
68 readings.
Step-by-step explanation:
We need to take this problem as a statistic problem where the normal distribution table help us.
We can start considerating that X is the temperature of the solution, then
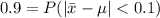
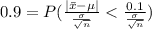
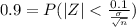
For a confidence level of 90% our
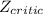 is 1.645
is 1.645
Therefore,
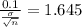
Substituting for
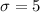 and re-arrange for n, we have that n is equal to
and re-arrange for n, we have that n is equal to
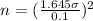
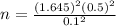
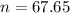

We need to make 68 readings for have a probability of 90% and our average is within
![0.1\°\frac]()