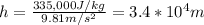Answer:
 m
m
B. No.
Step-by-step explanation:
mgh = mLf
mgh is the gravitation potential energy and mlf is the product of the mass of ice and its heat of fusion.
Where,
m is the mass
g is the acceleration of gravity
h is the height of drop
and Lf is the heat of fusion of ice
since the masses on both side of the equation can be cancelled out (also the reason to part B of the question), we are left with
gh=Lf
h=Lf/g