Answer:
B: conversion of energy stored in the chemical bonds of glucose to an energy from that the cell can use.
Step-by-step explanation:
Cellular respiration is a catabolic reaction through which cells get the required energy to run its activities. Cellular respiration can be divided into two;
- The one that can only happen in the presence of oxygen, often known as aerobic respiration,
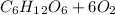 ------->
------->
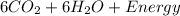
- The one that does not require oxygen, otherwise known as anaerobic respiration.
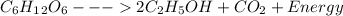
Be it aerobic or anaerobic, the energy stored in the chemical bonds of glucose ends up being converted to usable energy by the cell in a series of chemical processes whose reactions have been summarized in the equations above.
The usable energy generated during cellular respiration is mainly stored in the form of Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP).
Correct option is B