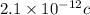Answer:
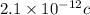
Step-by-step explanation:
We are given that
Surface area of membrane=
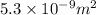
Thickness of membrane=
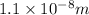
Assume that membrane behave like a parallel plate capacitor.
Dielectric constant=5.9
Potential difference between surfaces=85.9 mV
We have to find the charge resides on the outer surface of membrane.
Capacitance between parallel plate capacitor is given by
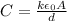
Substitute the values then we get
Capacitance between parallel plate capacitor=
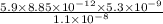
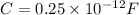
V=
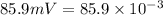
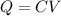
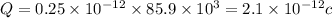
Hence, the charge resides on the outer surface=