Answer:
T₂ = 43.46 °C
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that:
The heat of the formation of carbon dioxide = - 393.5 kJ/mol (Negative sign suggests heat loss)
It means that energy released when 1 mole of carbon undergoes combustion = 393.5 kJ = 393500 J
Heat gain by water = Heat lost by the reaction
Thus,
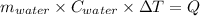
For water:
Mass of water = 5100 g
Specific heat of water = 4.18 J/g°C
T₁ = 25 °C
T₂ = ?
Q = 393500 J
So,
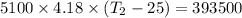
T₂ = 43.46 °C