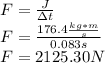Answer:
(a)
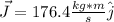
(b)
Step-by-step explanation:
(a) According to the law of conservation of energy, the potential energy of the person at 0.40 m is equal to its kinetic energy before the colision with the floor:
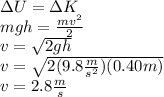
This is the initial velocity in the negative y-direction. Impulse is given by:
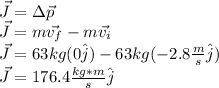
(b) The average force is: