Step-by-step explanation:
a) Balloon is being thrown down and is speeding up;
mg >
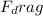
b) Balloon is in the air on its way down and moving with constant speed.
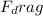 =mg
=mg
c) The Balloon is on the ground and rest instantaneously
mg = Normal
d) Balloon is moving slowly downward;
e) Because, at the peak of trajectory drag force is 0.
Drag force = 0