Answer:
For a: The value of
 for the given reaction is 271.6
for the given reaction is 271.6
For b: The value of
 for the reaction is 6.32
for the reaction is 6.32
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the number of moles, we use the equation:
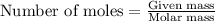 .....(1)
.....(1)
- For
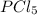 :
:
Given mass of
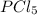 = 0.105 g
= 0.105 g
Molar mass of
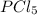 = 208.24 g/mol
= 208.24 g/mol
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
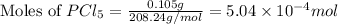
- For
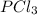 :
:
Given mass of
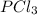 = 0.220 g
= 0.220 g
Molar mass of
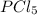 = 137.33 g/mol
= 137.33 g/mol
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
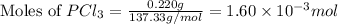
- For
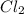 :
:
Given mass of
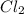 = 2.12 g
= 2.12 g
Molar mass of
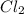 = 71.0 g/mol
= 71.0 g/mol
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
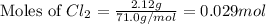
Volume of the flask = 25.0 L
For the given chemical equation:
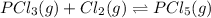
The equation used to calculate concentration of a solution is:
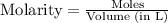
The expression of
 for above reaction follows:
for above reaction follows:
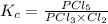
We are given:
![[PCl_5]=(5.04* 10^(-4)mol)/(25L)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/qxromoupzbo4ekmwn8g4dgvqd6jncvg7o8.png)
![[PCl_3]=(1.60* 10^(-3)mol)/(25L)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/ztdklx29flwdna7k504sudc4525adnqbf2.png)
![[Cl_2]=(0.029mol)/(25L)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/ji6qp09dsd2ml20unsq1we5qua599zrzql.png)
Putting values in above equation, we get:
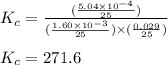
Hence, the value of
 for the given reaction is 271.6
for the given reaction is 271.6
Relation of
 with
with
 is given by the formula:
is given by the formula:
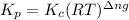
where,
 = equilibrium constant in terms of partial pressure = ?
= equilibrium constant in terms of partial pressure = ?
 = equilibrium constant in terms of concentration = 271.6
= equilibrium constant in terms of concentration = 271.6
R = Gas constant =
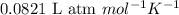
T = temperature =
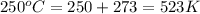
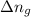 = change in number of moles of gas particles =
= change in number of moles of gas particles =
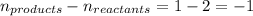
Putting values in above equation, we get:
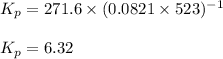
Hence, the value of
 for the reaction is 6.32
for the reaction is 6.32