Answer:
The mass of excessive water (H₂O) is 40.815 kg
Step-by-step explanation:
The Equation for the reaction is;
Li₂O(s) + H₂O(l) → 2LiOH(s)
From the question;
Mass of water removed is 80.0 kg
Mass of available Li₂O is 65.0 kg
We are required to calculate the mass of excessive reagent.
Step 1: Calculating the number of moles of water to be removed
Moles = Mass ÷ Molar mass
Molar mass of water = 18.02 g/mol
Mass of water = 80 kg (but 1000 g = 1kg)
= 80,000 g
Therefore;
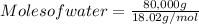
= 4.44 × 10³ moles
Step 2: Moles of Li₂O available
Moles = mass ÷ molar mass
Mass of Li₂O available = 65.0 kg or 65,000 g
Molar mass Li₂O = 29.88 g/mol
Moles of Li₂O = 65,000 g ÷ 29.88 g/mol
= 2.175 × 10³ moles Li₂O
Step 3: Mass of excess reagent
From the equation; Li₂O(s) + H₂O(l) → 2LiOH(s)
1 mole of Li₂O reacts with 1 mole of water to form two moles of LiOH
The ratio of Li₂O to H₂O is 1:1
- Thus, 2.175 × 10³ moles of Li₂O will react with 2.175 × 10³ moles of water.
- However, the number of moles of water to be removed is 4.44 × 10³ moles but only 2.175 × 10³ moles will react with the available Li₂O.
- This means, Li₂O is the limiting reactant while water is the excessive reagent.
Therefore:
Moles of excessive water = 4.44 × 10³ moles - 2.175 × 10³ moles
= 2.265 × 10³ moles
Mass of excessive water = 2.265 × 10³ moles × 18.02 g/mol
= 4.0815 × 10⁴ g or
= 40.815 kg
Thus, the mass of excessive water is 40.815 kg