Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
Problem 1:
Plants utilize light energy in the photosynthesis process to synthesize glucose, C₆H₁₂O₆, from CO₂ and H₂O by way of the reaction 6CO₂ +6H₂O → C₆H₁₂O₆ +60₂. How many grams of CO₂ are consumed in the production of 90 g of glucose?
Given parameters:
Mass of glucose = 10g
Unkown:
Mass of CO₂ consumed = ?
Solution:
The reaction equation is given as:
6CO₂ + 6H₂O → C₆H₁₂O₆ +60₂
- To solve this problem, the mole concept is a good approach. First work from the known to the unkown. The known is the given parameter which is the mass of glucose.
- Using the mass of glucose, estimate its number of moles and compare to that of the unknown carbon dioxide gas.
- Then find the mass from the obtained number of moles.
##
Number of moles of C₆H₁₂O₆ =
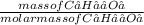
given that atomic weight of:
C = 12.01g/mol
H = 1.01g/mol
O = 16.00g/mol
Molar mass of C₆H₁₂O₆ = (6 x 12.01) + (12 x 1.01) + (6 x 16) = 180g/mol
Number of moles =
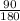 = 0.5mol
= 0.5mol
##
from the reaction equation,
1 mole of glucose is formed from 6 moles of CO₂
0.5 mole of glucose would be formed from (6 x 0.5)mole = 3moles
##
mass of CO₂ = number of moles x molar mass
molar mass of CO₂ = 12 + 2(16) = 44g/mol
mass of CO₂ = 3 x 44 = 132g of CO₂
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Problem 2:
For the reaction of 100.0 g of NaOH with Cl₂, 2NaOH + Cl₂ → NaClO + NaCI +H₂O, give the masses of each of the products.
Given parameters:
Mass of NaOH = 100g
Unknown:
mass of NaClo = ?
mass of NaCl = ?
mass of H₂O = ?
Solution:
Use the same procedure as highlighted in problem 1:
equation of reaction:
2NaOH + Cl₂ → NaClO + NaCI +H₂O
##
Number of moles of NaOH =
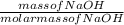
Molar mass of NaOH:
Atomic weight of Na = 23g/mol
Atomic weight of O = 16g/mol
Atomic weight of H = 1g/mol
Molar mass of NaOH = 23 + 16 + 1 = 40g/mol
Number of moles of NaOH =
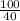 = 2.5mole
= 2.5mole
##
From the equation;
first product NaClO:
2 moles of NaOH produced 1 mole of NaClO
2.5 moles of NaOH will produce
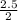 mole = 1.25mole of NaClO
mole = 1.25mole of NaClO
mass of NaClO = number of moles x molar mass
molar mass of NaClO = 23 + 35.5 + 16 = 74.5g/mol
mass of NaClO = 1.25 x 74.5 = 93.13g of NaClO
Second product NaCl:
2 moles of NaOH produced 1 mole of NaCl
2.5 mole of NaOH will produce 1.25 mole of NaCl
mass of NaCl = number of moles x molar mass
Molar mass of NaCl = 23 + 35.5 = 58.5g/mol
mass of NaCl = 1.25 x 58.5 = 73.13g of NaCl
Third product H₂O:
2 moles of H₂O produced 1 mole of H₂O
2.5 mole of H₂O will produce 1.25 mole of H₂O
mass of H₂O = number of moles x molar mass
molar mass of H₂O = 2(1) + 16 = 18g/mol
mass of H₂O = 1.25 x 18 = 22.5g of H₂O
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Hydrochloric acid (HCl gas dissolved in water) reacts with calcium carbonate in piece of limestone as follows: CaCO₃ + 2HCI → CaCl₂ + CO₂ + H₂0. If 14.6 g of CO₂ are produced in this reaction, what is the total mass of reactants and the total mass of the products?
Given parameters:
Mass of CO₂ = 14.6g
Unkown:
Total mass of products = ?
Total mass of reactants =?
Solution:
Total mass of products = mass of CaCl₂ + mass of CO₂ + mass of H₂O
Total mas of reactants = mass of CaCO₃ + mass of HCl
Using the procedures highlighted in the first problem, solve for the number of moles of the known:
##
Number of moles of CO₂ =
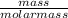
molar mass of CO₂ = 12 + 2(16) = 44g/mol
Number of moles of CO₂ =
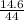 = 0.33mole
= 0.33mole
##
number of moles of all species:
These species are in a ratio of one to one and the will have the same number of moles as that of the known:
Number of moles of CaCl₂ = 0.33mole
Number of moles of H₂O = 0.33mole
Number of moles of CaCO₃ = 0.33mole
For HCl:
1 mole of CO₂ is produced from 2 moles of HCl
0.33 mole of CO₂ will produce 2 x 0.33moles = 0.66moles of HCl
##
Mass of each species:
Mass = number of moles x molar mass
molar mass of CaCl₂ = 40 + 2(35.5) = 111g/mol
molar mass of H₂O = 2(1 ) + 16 = 18g/mol
molar mass of CaCO₃ = 40 + 12 + 3(16) = 100g/mol
molar mass of HCl = 1 + 35.5 = 36.5g/mol
mass of CaCl₂ = 0.33 x 111 = 36.83g
mass of H₂O = 0.33 x 18 = 5.94g
mass of CaCO₃ = 0.33 x 100 = 33g
mass of HCl = 0.66 x 36.5 = 24.09g
##
Total mass of reactants = 33g + 24.09g = 57.1g
Total mass of products = 36.83g + 14.6g + 5.94g = 57.3g