Answer:
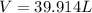
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
Starting by the ideal gas law which always involves absolute temperatures:
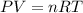
At the initial given conditions, the moles are computed, assuming they are constant:
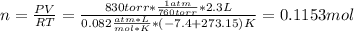
Now, by solving for the volume at the new pressure and temperature we get:
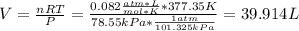
Best regards.